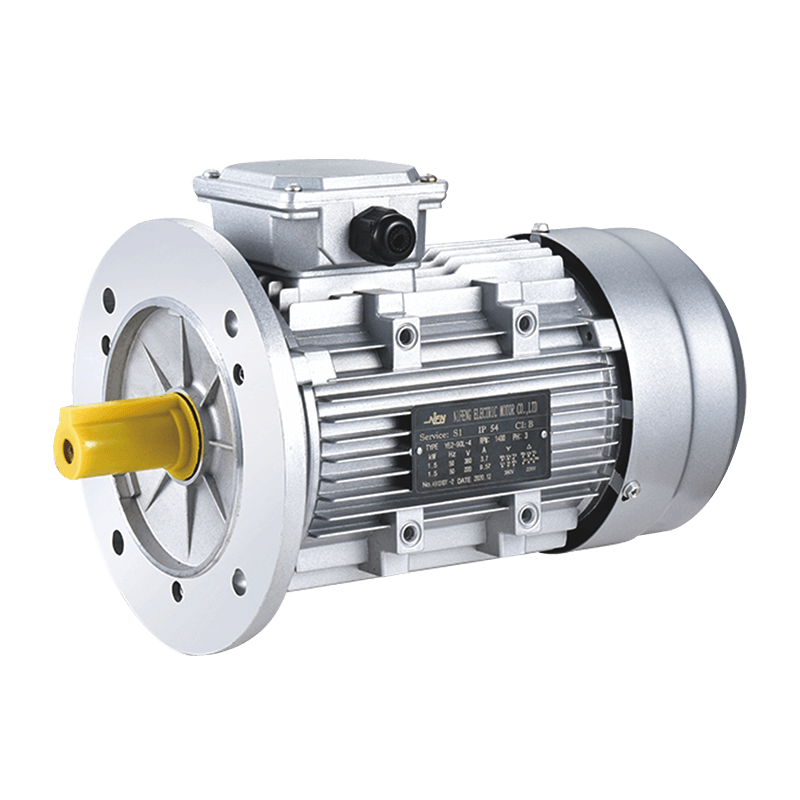
Let's start with the dimension of weight. Aluminum housings are much less dense than cast iron, only about one-third as dense. This means that the weight of a High-Efficiency Aluminum Case Induction Motor can be significantly reduced while providing the same protection. The aluminum case design makes the entire machine approximately 30% lighter than a cast iron case motor of the same power.
This lightness not only makes the motor easier to transport and install but also reduces the energy consumption of the motor during operation. According to one study, aluminum-cased motors consume about 5% less energy than cast-iron-cased motors under the same load. Therefore, the High-Efficiency Aluminum Case Induction Motor shows extraordinary strength in energy saving and emission reduction under its lightweight body.
Next, let's talk about heat dissipation. Aluminum is a good thermal conductive material, and its thermal conductivity is much better than cast iron. This means that the heat generated when the motor is working can be quickly transferred to the outside world through the aluminum shell, thus keeping the temperature inside the motor within a reasonable range. Taking a certain High-Efficiency Aluminum Case Induction Motor as an example, after 2 hours of continuous operation, the temperature of the aluminum case surface was only about 20°C higher than the ambient temperature, while the temperature of the cast iron case motor was about 40°C higher.
This efficient heat dissipation mechanism not only extends the life of the motor but also improves its working efficiency. It has been tested that under the same operating conditions, the efficiency of aluminum-cased motors is about 3% higher than that of cast-iron-cased motors. As a result, High-Efficiency Aluminum Case Induction Motor shows outstanding stability and reliability in applications that require long hours of continuous operation, such as industrial production lines and data centers.