Carbide edge tools are widely recognized for their contribution to clean and stable cutting across various manufacturing sectors. The application of a carbide edge in cutting tools stems from the need to maintain sharpness under prolonged operational stress. Compared with standard tool materials, carbide offers higher resistance to deformation at elevated temperatures, allowing it to retain structure when cutting hard materials.
Many industrial cutting tools integrate a carbide edge to reduce wear and extend usage cycles. This is especially beneficial in environments where metal, composite, or dense plastic materials are processed repeatedly. The hardness of a carbide edge allows it to penetrate these surfaces with reduced friction and less tool pressure, which can help maintain dimensional accuracy in machined parts.
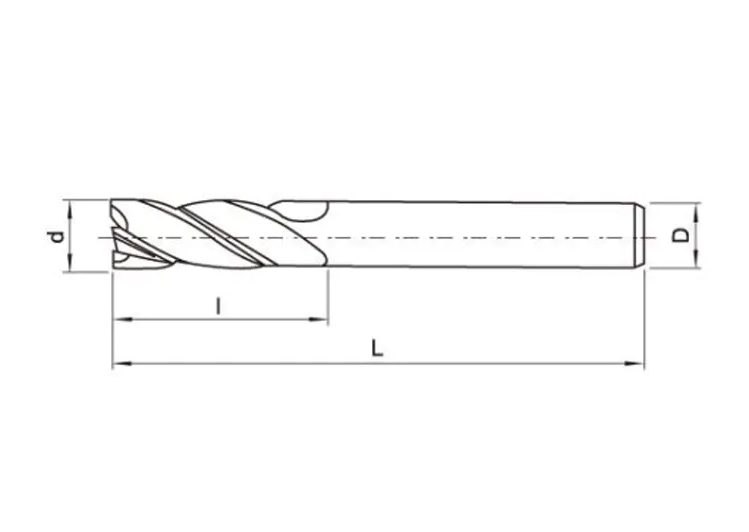
Manufacturers often choose carbide edge components for turning, milling, or drilling applications where tool consistency is critical. In CNC machining, for example, a stable carbide edge ensures predictable tool behavior and surface finish. It also supports faster cutting speeds, which can contribute to improved production efficiency over time.
Another advantage of using a carbide edge is its compatibility with advanced coatings that further reinforce the tool’s surface. These coatings can increase resistance to oxidation, thermal fatigue, and adhesion of material residues. Together, the combination of carbide and coating contributes to the extended function of precision tools.
Maintenance procedures also benefit from tools made with a carbide edge. Their durability reduces the frequency of regrinding or replacement, supporting lower tool turnover in industrial settings. As industries continue to emphasize production consistency, carbide edge solutions are positioned as a reliable component in many modern machining processes.